XB-IMG-23911
Xenbase Image ID: 23911
|
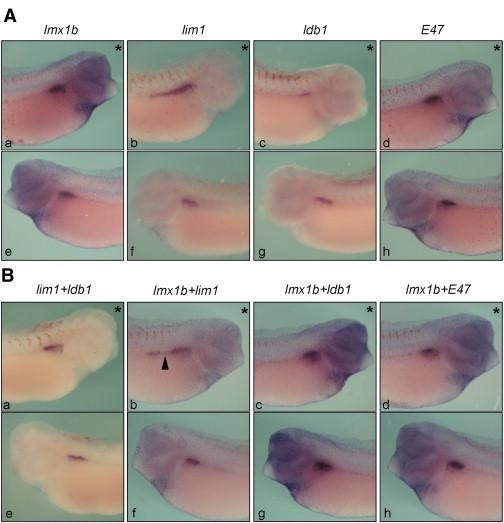
Fig. 5. Over-expression of lmx1b and its potential binding partners affects wt1 expression. mRNAs of lmx1b and its potential binding partners were injected either alone (panel A) or in combination (panel B), together with lacZ, into one V2 blastomere at the 8-cell stage. Red Gal staining followed by wt1 in situ hybridisation was carried out at stage 35/36 in order to assess any glomus phenotype. For each embryo, the injected side (indicated by an asterisk, panels aâd) was compared to the uninjected side (panels eâh). Injection of lmx1b mRNA alone did not induce any significant glomus phenotype (A, compare panel a to e), whereas injection of lim1 or ldb1 alone, its potential binding partners, resulted in the formation of an enlarged and reduced glomus respectively (A, b and f; A, c and g). These phenotypes can be partially rescued by the co-injection of lmx1b (B, b, arrowhead and f; B, c and g). Interestingly, co-injection of lim1 and ldb1 rescued both phenotypes, resulting in the formation of a more normal glomus (B, a and e). Injection of E47 alone or in combination with lmx1b did not induce any statistically significant phenotype (A, d and h and B, d and h). Image published in: Haldin CE et al. (2008) Copyright © 2008. Image reproduced with permission of the Publisher, Elsevier B. V.
Image source: Published Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
