XB-IMG-77508
Xenbase Image ID: 77508
|
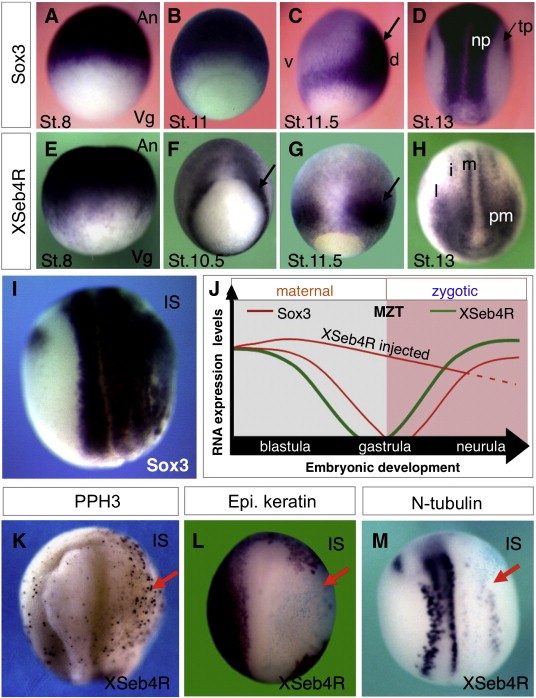
Fig. 1. Perturbed Sox3 maternal mRNA degradation upon XSeb4R overexpression leads to increased cell proliferation and inhibition of cell differentiation. Compared expression patterns of XSeb4R and Sox3 were monitored by wholemount in situ hybridization (WMISH), using Xenopus albino embryos at the indicated stages (St.) of development. Signals corresponding to these factors (black color) overlap in the animal pole derived cells of blastula embryo, oriented animal pole (An) up and vegetal pole (Vg) down (A, E). These maternal mRNA signals decline sequentially at gastrula stage (B and F, C and G). At these stages, signals of zygotic mRNAs are indicated with arrows; in panel C the embryo is oriented dorsal (d) right and ventral (v) left; in panels F and G the embryos are oriented dorsal side in front and the zygotic XSeb4R mRNA signal marks the differentiating mesoderm tissue. Zygotic Sox3 mRNA signal delineates the neural plate (np) and the trigeminal placodes (tp) at open neural plate stage, oriented dorsal side in front (D). At this stage, XSeb4R signals appear, in addition to the presomitic mesoderm (pm), in primary neuron precursors: medial, m (motor neuron); intermediate, i (interneuron) and lateral, l (sensory neuron). The timing of these expression characteristics as well as the phenotype described below are schematically illustrated in panel J. Capped-XSeb4R RNA was injected into two micromeres (200 pg each) of 4- or 8-cell stage embryos and analyzed by WMISH at neurula stage using Sox3 probe. XSeb4R overexpression leads to: robust ectopic Sox3 expression (I, 100%, n = 80); suppression of an epidermal marker (L, 100%, n = 56); suppression of expression (red arrows) of a neuronal marker gene N-tubulin (M, 100%, n = 50). Immunostaining of XSeb4R-injected embryos using an anti-phosphohistone H3 antibody revealed increased proliferation (red arrow; K, 63%, n = 76). In panels K, L and M embryos are oriented anterior side up with the injected side (IS) on the right. The blue staining (tracer) corresponds to the distribution of XSeb4R injected RNA marked by Xgal/LacZ enzymatic reaction. Image published in: Bentaya S et al. (2012) Copyright © 2012. Image reproduced with permission of the Publisher, Elsevier B. V.
Image source: Published
Larger Image Printer Friendly View |
