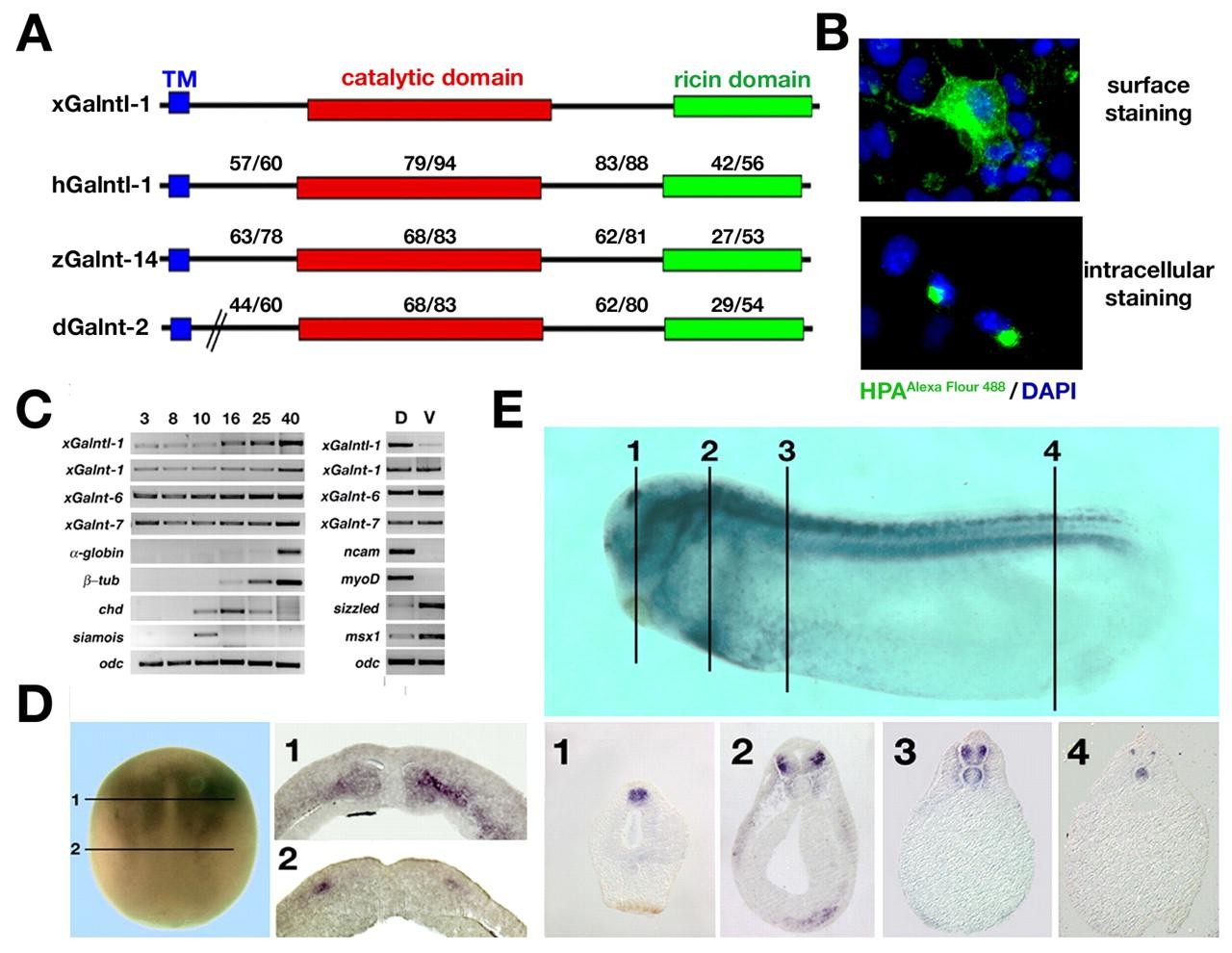
Fig. 1. Sequence and expression of xGalntl-1. (A) Comparison of Xenopus Galntl-1, human GALNTL1 (hGalntl-1), zebrafish Galnt14 (zGalnt-14) and Drosophila Galnt2 (dGalnt-2) protein sequences. The transmembrane domain (TM, blue), the catalytic domain (red), the Ricin domain (green) and amino acid identities/similarities for the different protein domains are indicated. (B) Detection of mucin-type glycosylation at the cell surface and in the Golgi compartment in xGalntl-1-transfected Cos-7 cells using Helix pomatia agglutinin (HPA) conjugated to Alexa Fluor 488. (C) RT-PCR analysis of xGalntl-1, xGalnt-1, xGalnt-6 and xGalnt-7 expression, using RNA from whole embryos (left) or dorsal and ventral marginal zone explants, isolated at gastrula stages and analysed at stage 20 (right). The blood markerα -globin, neural marker β-tubulin, dorsal mesodermal marker chordin and the nieuwkoop centre-specific gene siamois were used as references for the indicated developmental stages. Dorsal (ncam, myoD) and ventral (sizzled, msx1) marker genes were used as controls for the marginal zone explants. (D) Whole-mount in situ hybridisation analysis of xGalntl-1 expression at stage 13. Numbered lines indicate the positions of vibratome sections that reveal xGalntl-1 expression in the anterior mesoderm and in the deep layer of the lateral neural plate. (E) In situ analysis of xGalntl-1 expression at stage 27. The paraffin sections below show specific expression of xGalntl-1 in the anterior brain (1), neural crest (2), mediolateral spinal cord (2-4) and notochord (3,4).
Image published in: Herr P et al. (2008)
Copyright © 2008. Image reproduced with permission of the Publisher and the copyright holder. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License.
| Gene | Synonyms | Species | Stage(s) | Tissue |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| galnt16.L | xGalntl-1 | X. laevis | Throughout NF stage 13 | mesoderm neural plate sensorial layer of neurectoderm |
| galnt16.L | xGalntl-1 | X. laevis | Throughout NF stage 27 | notochord brain spinal cord pineal gland heart primordium dorsal lateral plate mesoderm midbrain |
Image source: Published
Permanent Image Page
Printer Friendly View
XB-IMG-3377